Dialysis Care Services
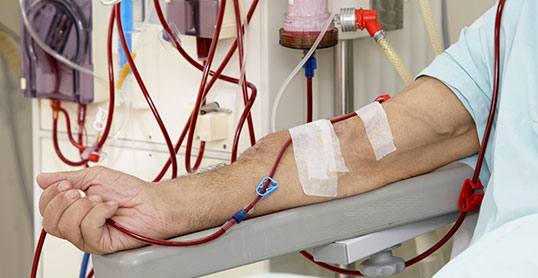
Hemodialysis is the most common type of dialysis. Patients visit a center to receive treatment.
Hemodialysis involves accessing the bloodstream through a surgically-prepared access site that allows blood to pass through a special filter of a dialysis machine, be cleansed and return to your body. Treatments are administered by well-trained medical professionals and highly- skilled technicians.

Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
Peritoneal dialysis, or PD, is a process by which a warmed solution called dialysate enters your peritoneal cavity (part of your abdominal cavity) through a small catheter that is surgically placed there as an access point. It absorbs wastes and excess fluid from your blood and is then drained and replaced with fresh dialysate.
Time Commitment: Peritoneal dialysis is usually performed at home on a daily basis, usually requiring 4 to 5 fill-and-drain exchanges each day, or at night while you are sleeping.
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD) is the most commonly used form of PD that functions much like your kidneys used to, cleansing the blood.

Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD)
Peritoneal dialysis, or PD, is a process by which a warmed solution called dialysate enters your peritoneal cavity (part of your abdominal cavity) through a small catheter that is surgically placed there as an access point. It absorbs wastes and excess fluid from your blood and is then drained and replaced with fresh dialysate.
Time Commitment: Peritoneal dialysis is usually performed at home on a daily basis, usually requiring 4 to 5 fill-and-drain exchanges each day, or at night while you are sleeping.
Automated Peritoneal Dialysis (APD) is performed at home with the help of a cycler machine, which cleanses your blood. This can be done during the day or night.
Home Dialysis Services
Hemodialysis involves accessing the bloodstream through a surgically-prepared access site that allows blood to pass through a special filter of a dialysis machine, be cleansed and return to your body.
Advantages:
- You have more control and greater flexibility about when and where you dialyze.
- You can dialyze in the comfort of your home with the help of a loved one.
- You can take a more active role in your treatment which has been proven to yield better outcomes.
- Health benefits can include more energy and better blood pressure control.


